What is Gout?
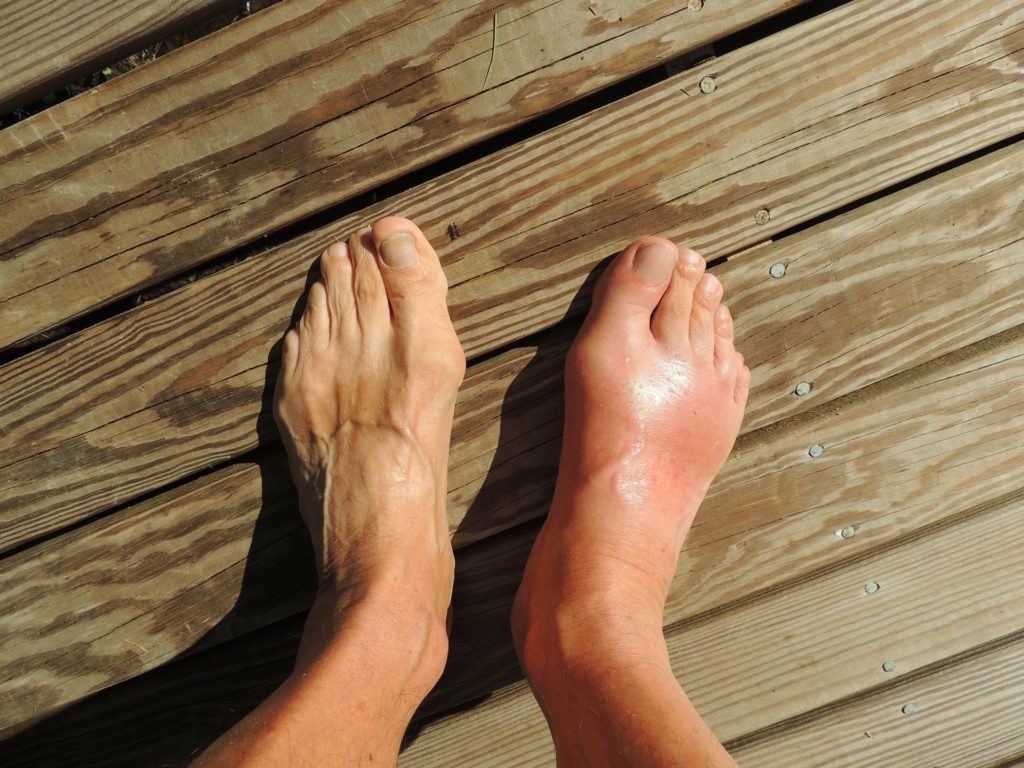
Gout is a complex type of arthritis that is characterized by severe attacks of pain, redness, swelling, and tenderness in joints, but most often in the big toe. Gout can affect anybody. An attack of gout can be severe to wake you up in the middle of the night with a burning feeling on your big toe. The joint is hot, swollen, and so tender that even the weight of the bedsheet on it might seem excruciating.
Gout symptoms are painful, but there are ways to manage symptoms and prevent flares. Gout is a painful metabolic disorder leading to inflammation and uric acid deposition in the joints’ cartilages. Gout affects the big toe first, causing it to swell and become extremely painful. It spreads into the ankles, knees, joints of hands and feet, the elbow and wrist in the upcoming phases.
Our body produces uric acid as it breaks down chemicals called purines, found naturally in our bodies and food. Typically, uric acid melts and goes via the urine through the kidneys. But if the body produces an excess of uric acid or the body isn’t excreting enough uric acid, it accumulates in the body. This buildup leads to the creation of sharp, needle-like crystals. When they collect in the joints or surrounding tissues, it causes pain, inflammation, and swelling.
Ayurvedic herbal home remedies for uric acid may give you a little relief, but it’s important to get treatment for the underlying root cause for long-term relief. Men are more prone to get Gout, but women become more prone to Gout after menopause.
See: Ayurvedic therapy herbs to increase breast milk to increase lactation
Gout Symptoms
Gout signs and symptoms are almost always acute, occurring abruptly frequently at night without warning. They include:
– Intense joint pain: Gout usually affects the large joint of the big toe, but it can happen on your feet, ankles, knees, wrists, and hands. The pain is likely to be acute within the first 12 to 24 hours after it starts.
– Inflammation: The affected joint or joints become red, swollen, and tender.
– Lingering distress: After the most severe pain dies down, some joint discomfort level may last up to two weeks. Later attacks may last longer and affect more joints.
Gout patients may experience repeated attacks of arthritis through the years. Uric acid crystals may deposit in miniature fluid-filled sacs (bursae) around the joints. These urate crystals may incite inflammation at the bursae, resulting in swelling and pain around the joints (a bursitis condition).
In the case of chronic Gout, nodular masses of uric acid crystals deposition in different soft-tissue regions of the body. Although they are most frequently seen as hard nodules around the fingers, in the ears, in the elbows’ tips, and around the big toe, tophi nodules can appear anywhere in the body. They’ve been reported in unexpected areas like vocal cords or around the spinal cord.
Causes
Hyperuricemia is the root cause of Gout. This can be due to an unhealthy diet, genetic predisposition, or underexcretion of urate. In a healthy person, uric acid melts in your bloodstream and passes through your kidneys into your urine. Renal underexcretion of uric acid is the principal cause of hyperuricemia in about 90 percent of cases, while overproduction cause results in less than 10%.
Along with an inherited abnormality in managing uric acid, other risk factors for developing Gout include excessive weight gain, abnormal kidney function, obesity, heavy alcohol consumption, high blood pressure, and eating too much meat and fish that are high in purines. Some medicines, like diuretics, can also cause Gout. Certain conditions can trigger acute attacks of Gout. These conditions include injury to the joints, fever, dehydration, excessive eating, and recent operations.
Risk Factors
The uric acid level in your body can rise due to many factors, including:
– Diet: Eating a diet full of seafood and meat and drinking beverages sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose) increases uric acid levels, which in turn increases your risk of Gout. Alcohol consumption, especially beer, also increases the risk of Gout.
– Obesity: Your body produces more uric acid if you are overweight, and your kidneys have a harder time removing uric acid.
– Medical conditions: Certain conditions can boost your risk of Gout. These include untreated hypertension and chronic conditions such as metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and kidney and heart ailments.
– Specific medications: Some medications can increase uric acid levels.
– Genetics: If other members of your household have had Gout, you are more likely to develop the illness.
– Age and gender: Gout occurs more frequently in men, primarily because women generally have lower uric acid levels. Women’s uric acid levels increase to levels like men’s after menopause. Men can develop Gout sooner – usually between the ages of 30 and 50 –whereas women generally develop symptoms and signs after menopause.
– Surgery: Experiencing recent surgery or injury was associated with a higher risk of developing a gout attack.
See: Ayurvedic treatment modalities for depresssion and mental disorders
Ayurveda Management of Gout
Vata Rakta or Aadya Vata is the classical name for Gout in Ayurveda, which suggests the existence of Vata, and it impacts raktdhatu (blood cells ). Vitiation (impairment) of Vata dosha and raktdhatu results from increased intake of hot, sour, salty, alkaline, heavy, and penetrating foods. The diminished doshas travel through the body’s channels and become accumulated at the smaller joints causing harm to the bones and tissues of the joint, leading to Vatarakt.
Excessive anger, waking up late in the nighttime, sleeping in the daytime, excessive traveling, injury, overindulgence in bodily exercises, excessive sexual activity, and suppressing the body’s natural urges may also cause Gout.
Several causes are recorded in Ayurveda, which induces Vatarakta are unhealthy diet and lifestyles such as drinking alcohol, daytime sleeping, excessive ingestion, buttermilk, incompatible foods such as fish with milk products, staying awake in the night, and anger.
Depending on the root cause of the disease, Vatarakta is categorized into two types.
– Uttana (shallow ) — This is situated in the tweak (epidermis ) & mama (muscle).
– Gambhira (deep) — This is located in the deeper dhatus and more acute. Tophi or nodule formation happens.
Ayurvedic treatment includes Panchakarma treatment together with internal medications, diet & lifestyle alterations. Therapies like Abhyanga swedam, Elakkizhi, Pizhichil, Snehapanam, Virechanam, Vasti, Navarakizhi, etc., are very helpful in treating or even curing Vatarakta.
Often, even Rakthamokshana treatment is also practiced for faster and long-lasting relief.
See: Ayurvedic treatment for frozen shoulder pain & alignment
Ayurvedic herbal remedies for gout
There are lots of Ayurvedic remedies for Gout and uric acid buildup. Some of these treatments are herbal, while some are lifestyle changes.
– Dietary changes: Ayurvedic treatments for Gout usually incorporate dietary modification. The two Ayurveda and Western medicine advocate was preventing or reducing alcohol, sugar, meat, and seafood. In Western medicine, these are known as high-purine foods, and they tend to increase the levels of uric acid. In Ayurveda, it is advised to cut out milk if you have Gout. Some Ayurvedic practitioners urge veganism to reduce uric acid levels.
– Exercise: Exercise is an important tenet of Ayurveda. It is believed that exercise, particularly yoga, supports general health. Western medicine agrees that there are a lot of health benefits of exercise. Since exercise is an established system of reducing anxiety, and anxiety is a frequent cause of gout attacks, it is no surprise that exercise is suggested for those who have Gout. Yoga particularly has been linked to lower levels of anxiety, based on some 2013 reviews of studies. Exercise itself may reduce uric acid. A study demonstrated that profuse sweating due to exercise reduces uric acid levels in the body. This action can be attributed to the concept that perspiration is how your body releases uric acid and purifies itself.
– Giloy: Giloy is a widely used herb in Ayurveda. A 2017 review about the health advantages of giloy states that “the juice extract from the stem of giloy helps to neutralize the increased uric acid levels in the body. That action makes it highly effective for the treatment of Gout. Another 2014 evaluation has indicated that giloy has anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving results on rodents. But more research is required before its benefits can be shown in humans.
– Neem: Neem is often utilized in Ayurveda to soothe gout flare-ups and decrease inflammation. A paste is made with neem and applied to the area affected by Gout.
– Triphala: Triphala, or “three fruits” in Sanskrit is a herbal treatment composed of three fruits: bibhitaki, Amalaki, and haritaki. Each is thought to impact the body’s three doshas. One of Triphala’s reported advantages is that it is an anti-inflammatory, so it might decrease the inflammation associated with Gout. Though some research has found that Triphala has anti-inflammatory properties, the study is limited to animal studies.
– Turmeric: Turmeric is a root that’s usually used as a spice. In Ayurveda, turmeric is thought to have many health benefits due to its active ingredient Curcumin. Turmeric is relatively safe and may be added to curries, soups, and much more. It is frequently consumed in Haldi doodh, also referred to as golden milk.
– Ginger: Among the most commonly used plants in Ayurveda, ginger has a variety of purported health benefits. It’s a favorite home cure for Gout. A study pointed that ginger works as an effective remedy for Gout, in addition to a range of other inflammatory conditions. Ginger can easily be added to a daily diet.
– Bitter gourd: Bitter gourd is usually recommended in Ayurveda for the treatment of Vata ailments. Therefore, it is often prescribed for treating Gout.
– Berries: Many Ayurvedic practitioners advocate adding cherries and dark berries into your diet to decrease uric acid amounts in the body. Cherry juice may help treat Gout. A study found that consuming cherry juice concentrate reduced uric acid levels. Additionally, it found that concentrated pomegranate juice reduced uric acid levels, even though it was not as successful as cherry juice.
See: Ayurvedic treatment modalities for depresssion and mental disorders
Summary
Ayurvedic herbal remedies are available for Gout. Always consult your doctor when using any new herbs or nutritional supplements or if undergoing a lifestyle change. Speak to an Ayurvedic practitioner before you try any Ayurvedic remedies for uric acid.